Gouty arthritis might not be an ailment that has been talked about as much as say, Diabetes, Obesity or Cancers, but it has been something man has been living with since ages. From King Louis XIV of France to Queen Anne of England to Sir Robert Walpole, Britain’s first Prime Minister—victims of gout were as commonplace then as it is now.
What is Gout and what causes it?
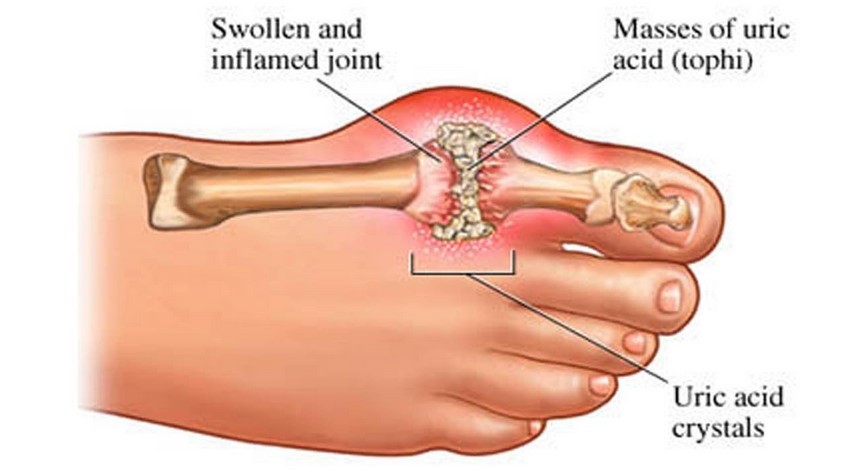
Simply put, Gout is a form of arthritis and is caused by an accumulation of excess uric acid in the bloodstream. Uric acid has no useful function in the human body and is a byproduct of the breakdown of a group of chemicals called purines, a basic building block of DNA, present body tissues and also in many foods. Accumulation of uric acid on its own is not a harmful affair and elevated levels of uric acid do not necessarily ensure a gout attack. However, when the excess levels of uric acid form hard crystals that get deposited in joints, tendons, and other tissues, the patient experiences intense pain in those areas.
Signs and symptoms
The most common manifestation of gout is acute arthritis, or severe pain in joints. Usually, the metatarsal-phalangeal joint, which is at the base of the big toe, is most commonly affected by gout, accounting for almost 50% of the cases. Other areas prone to attack include the forefoot, instep, heel, ankle, and knee. The attack typically begins abruptly, often at night, and the pain is accompanied by swelling and redness in the affected area. Sometimes, the intensity of the pain can cause other ailments like fever, flu or muscle aches.
A man’s disease
Although all humans are at risk of gout, it is mostly seen in men past adolescence. It is rarely seen in women before menopause, as estrogen protects women from developing gout until after menopause when the estrogen levels fall.
You are also prone to gout if your family holds a history of an affected. Your medical history such as if you have undergone an organ transplant, or regularly take medicines such as diuretics, aspirin, cyclosporine, or levodopa, the vitamin niacin, also increase your risk of being affected.
Gout left untreated usually increases the frequency of attacks, and over time, uric acid crystals form gritty, chalky nodules called tophi, that may need to be surgically removed. Further neglect of gout could also result in serious issues such as joint deformity, kidney stones (formed by the same urate crystals), and as a result kidney disease and kidney failure.
What to do in the middle of an attack
- Rest the affected joint in an elevated position until the bout of pain reduces.
- Use ice compression to ease the discomfort and reduce the swelling.
- For pain relief, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs could be taken; however, avoid drugs like aspirin that are high in purines.
- Do not neglect gout attacks for too long. Consult a rheumatologist and get a joint fluid analysis done before the problem gets recurrent.
Watch what you eat
Gouty arthritis also affects overweight people or those who have weight-related health issues including diabetes and high blood pressure or cholesterol. Dietary causes also account for about 12% of gout. Alcoholic drinks, especially beer, and organ meats such as liver and seafood and oily sea fish like anchovies and sardines, are high in purines. Therefore it is of utmost importance to maintain a general healthy and balanced diet and an effective exercise routine to keep body weight in control throughout the year, so as to reduce the chances of painful gout attacks.
Consulting a certified nutritionist is mandatory so as to have a clear knowledge of which foods to avoid or eat in moderation that would address the requirement of maintaining a healthy weight, yet that are not high in purines.

 Prep Time: 10 minutes
Prep Time: 10 minutes Cook Time: 15 minutes
Cook Time: 15 minutes Total Time: 25 minutes
Total Time: 25 minutes