Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. It encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. Despite significant advancements in medical science, the question remains: can cardiovascular disease be cured?
In this blog, we will delve into the complexities of CVD, exploring treatment options, the role of a cardiac nutritionist, and the possibility of a cure.
What is Cardiovascular Disease?
Cardiovascular disease refers to a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, and stroke. These conditions often arise due to a buildup of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of complications.
Types of Cardiovascular Disease
CVD encompasses various conditions, each with its own set of symptoms and complications. Common types include coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertension, and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Causes of Cardiovascular Disease
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, significantly contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. These factors can lead to obesity, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure, all of which increase the risk of CVD. By consulting an experienced cardiologist nutritionist, you will learn the crucial lifestyle modifications you must make to reduce the chances of cardiac problems.
Genetic Factors
Genetics also play a role in cardiovascular health, with certain genetic predispositions increasing the likelihood of developing CVD. Family history of heart disease, genetic mutations, and inherited conditions like familial hypercholesterolemia can all influence an individual’s risk.
Treatment Options
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing cardiovascular disease by controlling symptoms, lowering blood pressure, and reducing the risk of complications. Common medications include statins, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and antiplatelet drugs.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medications, lifestyle modifications are essential for managing CVD. These may include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
Surgical Procedures
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat cardiovascular disease. Procedures such as angioplasty, bypass surgery, and valve repair or replacement can help improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms.
The Role of Nutrition
Importance of a Healthy Diet
Diet plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular health, influencing various risk factors such as cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and weight. According to the recommendations of cardiac nutritionists, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help prevent and manage CVD.
Cardiac Nutritionist’s Perspective
Consulting a cardiac nutritionist can provide personalized dietary recommendations tailored to individual needs and medical conditions. These professionals offer guidance on nutrient-rich foods, portion control, and meal planning strategies to support heart health.
Best Diet for High Blood Pressure
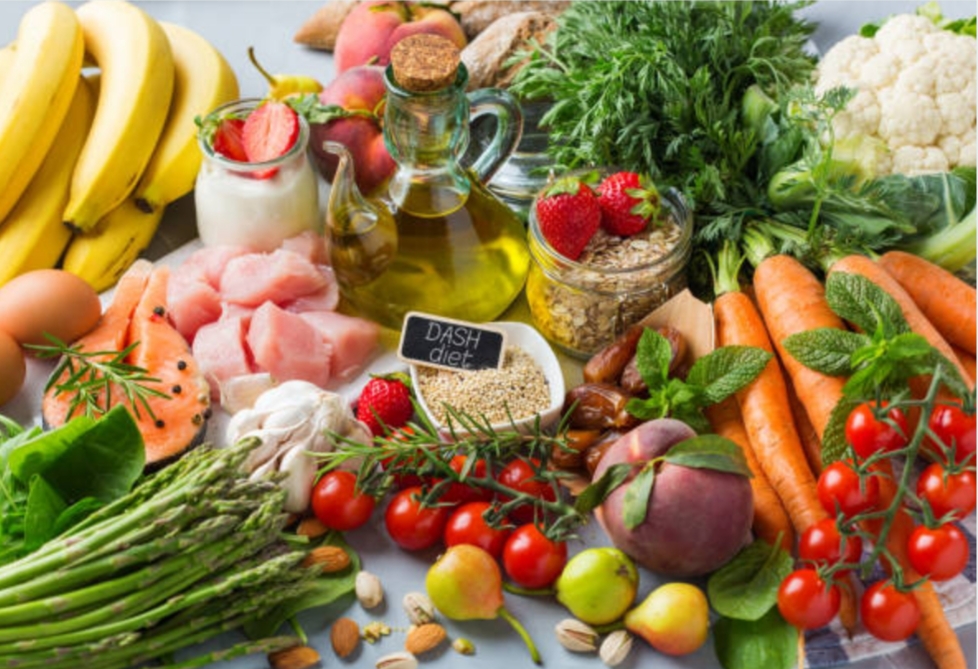
DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is renowned for its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure. Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, the DASH diet promotes a balanced approach to nutrition.
Mediterranean Diet
Similarly, the Mediterranean diet is celebrated for its heart-healthy benefits. Rich in olive oil, nuts, fish, and whole grains, this diet emphasizes plant-based foods and healthy fats, which can help reduce the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions.
Exercise and Cardiovascular Health
Importance of Physical Activity
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of CVD. Physical activity helps strengthen the heart, improve circulation, and control weight, leading to better overall health outcomes.
Types of Cardiovascular Exercises
Aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are particularly beneficial for heart health. These activities increase heart rate and improve endurance, contributing to a stronger, healthier cardiovascular system.
Prevention Strategies
Risk Factor Modification
Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the incidence of cardiovascular disease. Managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity through lifestyle changes and medications can significantly lower the risk of CVD.
Regular Health Checkups
Regular health screenings and checkups are essential for early detection and management of cardiovascular risk factors. Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar can help identify potential issues before they escalate into serious health problems.
Can Cardiovascular Disease be Cured?
Managing Symptoms vs. Curing the Disease
While advancements in medical treatment have improved outcomes for individuals with cardiovascular disease, a definitive cure remains elusive. Current therapies focus on managing symptoms, reducing risk factors, and preventing complications rather than curing the underlying condition.
Challenges in Curing Cardiovascular Disease
The complex nature of cardiovascular disease, coupled with individual variations in genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, poses significant challenges to finding a universal cure. Moreover, the progressive nature of certain conditions, such as atherosclerosis, makes complete eradication difficult.
Promising Therapies
Despite the obstacles, ongoing research continues to explore innovative approaches to treating cardiovascular disease. From stem cell therapy and gene editing techniques to novel drug therapies and targeted interventions, there is hope for future breakthroughs in CVD treatment.
Future Prospects
As our understanding of cardiovascular disease deepens and technology advances, the prospect of finding a cure grows more promising. By addressing the root causes of CVD, harnessing the body’s natural healing mechanisms, and developing personalized treatment strategies, researchers aim to revolutionize the management of cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
While cardiovascular disease remains a prevalent and formidable health challenge, significant strides have been made in its treatment and prevention. While a definitive cure may still be on the horizon, adopting a proactive approach to heart health through lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring can greatly improve outcomes and enhance quality of life for individuals living with CVD. If you have been planning to consult a reputable cardiac nutritionist, connect with Food & Wellness. Our experienced team of cardiologist nutritionists offers the best diet plans for high blood pressure, diabetes, thyroid, and other health conditions. We provide both in-person and online consultations. Book an appointment today.