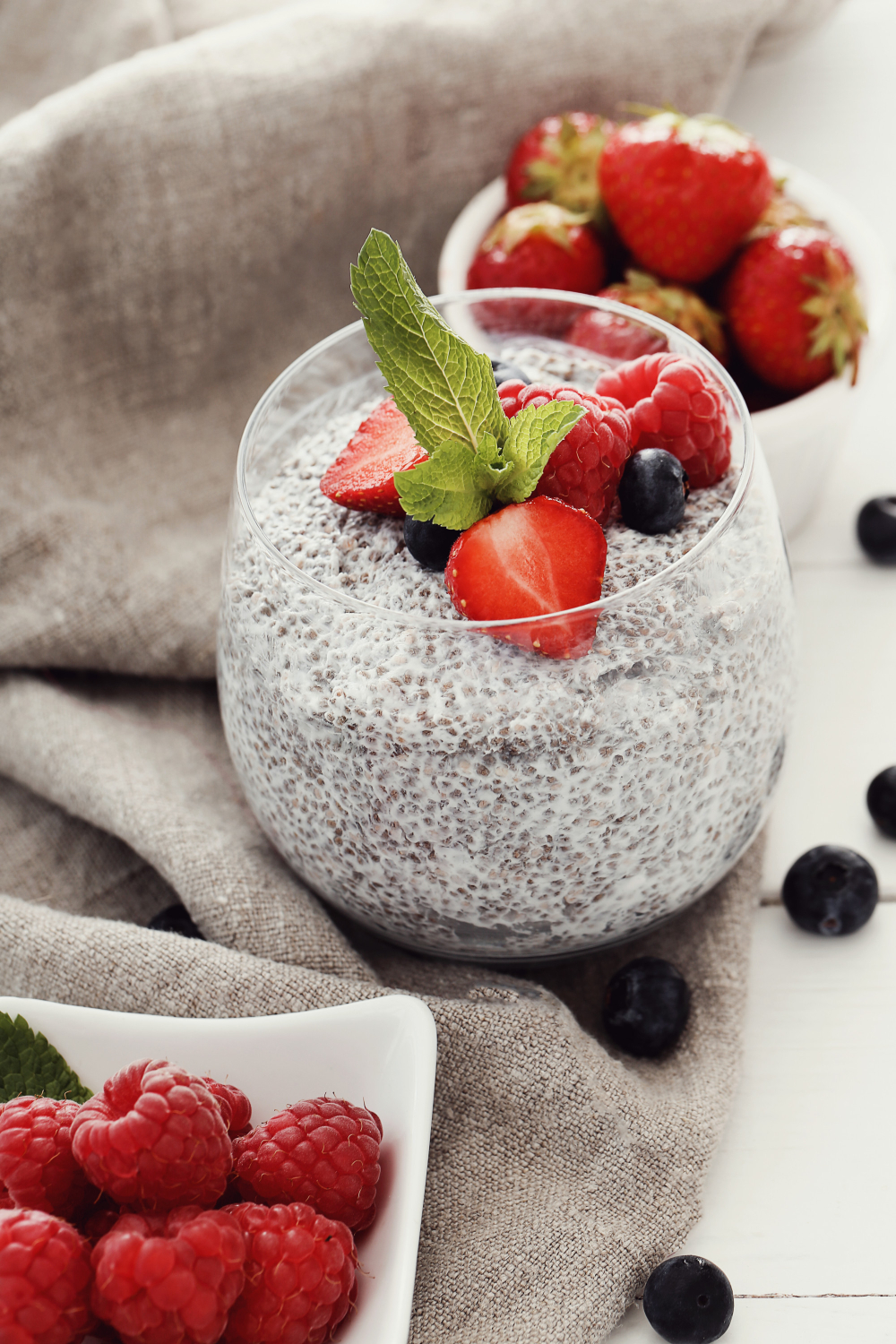
Berry Chia Pudding
-
 Prep Time: 5-6 Minute
Prep Time: 5-6 Minute -
 Total Time: 5-6 Minute
Total Time: 5-6 Minute -
 Yield: 1 -2 Serving 1x
Yield: 1 -2 Serving 1x -
 Category: Breakfast
Category: Breakfast -
 Method: Blending method
Method: Blending method
Description
Berry chia pudding is a filling dessert with many health advantages. It is also tasty and healthy. Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fibre included in chia seeds can help with digestion, enhance heart health, and lessen inflammation. A boost in vitamins and minerals, including potassium and vitamin C, which helps promote immune function and control blood pressure, is given by the antioxidant-rich berries that were added to the custard. Furthermore, because they are low in calories and high in fibre, which can keep you feeling fuller for longer, the combination of chia seeds and berries can aid in the promotion of good weight control. Overall, having berry chia pudding on a daily basis can support a balanced, nutrient-rich diet, enhancing overall health and wellness.
Ingredients
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 2 tablespoons chia seeds
- 1/2 teaspoon almond extract
- 1 cup mixed berries (such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries)
- 2 tablespoons crushed almonds or other nuts for toping
- 1 tablespoon honey
Instructions
- In a bowl, whisk together the almond milk, chia seeds, honey and almond extract until well combined.
- Let the mixture sit for about 5 minutes to allow the chia seeds to absorb the liquid, then whisk again to break up any clumps.
- Cover the bowl and refrigerate for at least 2 hours or overnight to allow the chia seeds to gel and thicken the pudding.
- After the chia pudding has set, blend the mixed berries in a blender or food processor until smooth.
- Layer the chia pudding and the berry puree in serving glasses or jars, starting with a layer of chia pudding followed by a layer of berry puree. Repeat until all the pudding and puree are used.
- Top with crushed almonds or other nuts for added crunch and texture.
Nutrition
- Serving Size: 1
- Calories: 235
- Fat: 10 g
- Carbohydrates: 15 g
- Fiber: 6.1 g
- Protein: 4.3 g
Keywords: Berry Chia Pudding






